In today’s rapidly evolving workplace, companies need employees who can adapt to shifting priorities, collaborate across disciplines, and solve complex problems. This is where the concept of T-shaped skills becomes invaluable. Originally popularized by Tim Brown of IDEO, T-shaped professionals possess deep expertise in one area, complemented by a broad understanding of related fields. These hybrid skill sets empower organizations to be more innovative, flexible, and collaborative.
What are T-Shaped Skills?
Imagine the letter "T." The vertical bar represents deep expertise or specialized knowledge in one discipline. For example, a software engineer with advanced coding abilities in Python or Java would have a strong vertical bar. The horizontal bar represents a broader understanding of adjacent fields, such as project management, UX design, or business strategy. This breadth of knowledge enables professionals to collaborate effectively with colleagues across other functions, making them versatile contributors.
Why T-Shaped Skills Matter
Enhanced Collaboration Across Teams
Cross-functional teams are the cornerstone of modern organizations. T-shaped individuals can step outside their specialized areas and understand the language, priorities, and pain points of other departments. Whether it's a marketing manager grasping the basics of data analytics or an IT expert appreciating user experience design, this adaptability fosters seamless collaboration. When employees work well across disciplines, they can collectively drive better outcomes.
Agility and Flexibility
In an era defined by digital transformation and evolving market demands, organizations need to pivot quickly. T-shaped professionals can transition between roles or projects more easily, helping organizations adapt to change without losing momentum. For instance, during times of resource constraints, a person with both a technical and project management background can manage timelines while contributing to technical decisions. This adaptability reduces the dependency on siloed expertise.
Innovation and Problem-Solving
Innovation often happens at the intersection of disciplines. A person with deep expertise in one area but a broad understanding of others can generate novel solutions by connecting ideas in ways that specialists in one domain might overlook. T-shaped professionals tend to ask more questions, explore unconventional solutions, and bring diverse perspectives to the table—all of which are crucial to fostering innovation in the workplace.
Better Understanding of the Bigger Picture
When employees can see how their work fits into the broader organizational goals, they are more engaged and motivated. T-shaped individuals with a broad knowledge base can appreciate the interconnectedness of different departments and strategies, which allows them to align their tasks with organizational priorities. This holistic view is essential for roles like product management, where understanding the needs of customers, engineers, and marketers is vital.
Improved Communication and Leadership
Leaders who possess T-shaped skills can communicate more effectively across teams and drive initiatives that require buy-in from multiple departments. They are also better equipped to make informed decisions that balance the needs of different areas of the business. These skills are critical in leadership roles, where success often depends on aligning diverse teams toward a common goal.
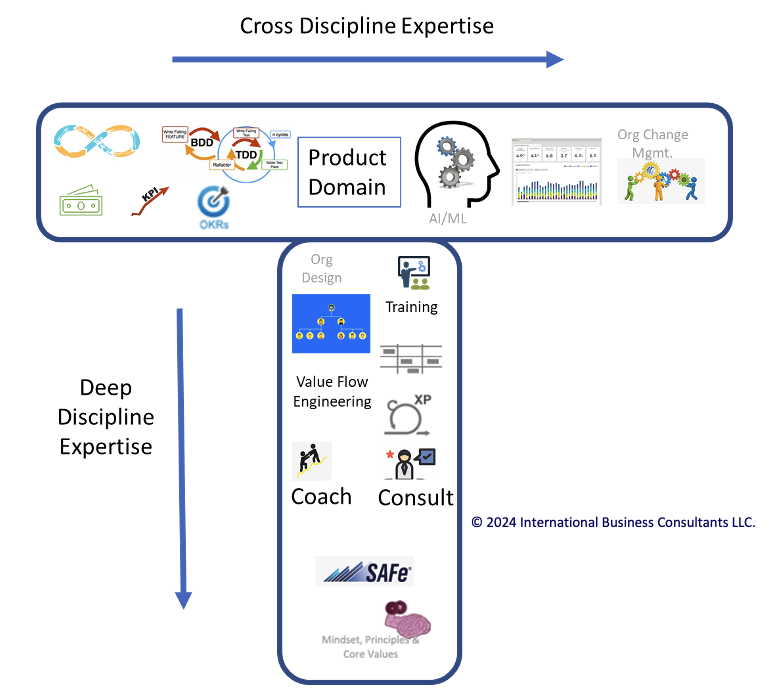
Cultivating T-Shaped Skills in Your Organization
While T-shaped skills are highly desirable, they don’t always occur naturally. Companies can take deliberate steps to cultivate these skills within their workforce:
- Cross-Training Programs: Encourage employees to engage in training outside their core discipline. For example, engineers could take courses in design thinking, or sales professionals could learn about data analytics.
- Job Rotation: Implementing rotational programs that allow employees to spend time in different departments helps them gain exposure to other areas of the business and fosters cross-functional collaboration.
- Mentorship and Coaching: Pair employees with mentors from different disciplines to encourage the exchange of knowledge and skills.
- Fostering a Learning Culture: Provide opportunities for continuous learning and create an environment where acquiring knowledge outside one’s domain is encouraged and rewarded.
Conclusion
In a world where collaboration and agility are critical to organizational success, T-shaped skills offer a competitive edge. These versatile employees can drive innovation, improve communication, and help teams navigate the complexities of modern business environments. Organizations that invest in cultivating T-shaped professionals will not only boost their problem-solving capabilities but also build a more resilient and adaptive workforce for the future.
More Insights

Illuminating the Role of the People Manager in SAFe: From Traditional Oversight to Empowered Enablement
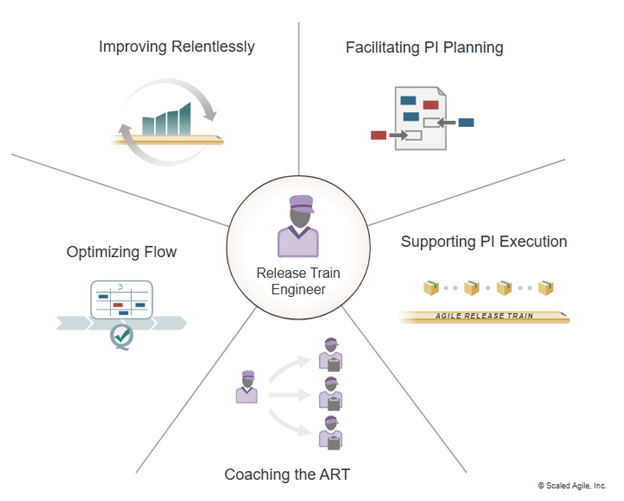
Demystify Role of RTE in SAFe

Revolutionizing Customer Experience with Generative AI: Personalization at Scale
